What is manufacturing?
Manufacturing is a process that converts raw materials into useful products. This process may have many steps to make a product furnished by using machines, human labor, and other tools like socks manufactured after many processes implemented on the cotton.
What is lean manufacturing?
A lean product is a product that has these basic qualities that make it lean.
What is a product?
A product is an item manufactured for the betterment of humans and it can also be sold. All products are furnished from raw materials, are in machines, and have a cost.
What is Lean Production?
Production has these qualities, which are the basics of lean manufacturing or lean production system, given below.
- Best Quality Product
- Deliver to the customer on Time
- Manufactured at Minimal Cast
- Manufactured in a Safe & Friendly Environment for employees.
Why do you need Lean Production?
Lean production is an industrialist’s priority because the main goal of Lean is to create more value with fewer resources. A lean production team strives to create proper roles that provide perfect value with zero waste. The basics of Lean manufacturing revolve around important factors involving all basic requirements.
We also call it the 4Ps of lean thinking.
- Performance
- Test and evaluate the production unit’s performance. Make bold decisions to increase performance. Create a mindset in your team for continuous improvements.
- People
- Empower your company supervisors and improve management decisions. Respect your people and respect your suppliers.
- Process
- Take the best process quality and eliminate waste and issues. Divide the workload into sections.
- Purpose
- Take your time to benefit and continuously improve with your mission and vision.
Quality Production
In today’s highly competitive market, the key to a successful business lies in fulfilling customer requirements with products of the highest quality. Product quality is not merely about meeting the basic specifications but involves exceeding customer expectations to foster loyalty and satisfaction.
Product quality is the first pillar of lean manufacturing. Implementing these techniques in our industry ensures that the quality of the product “fulfills customer requirements.”
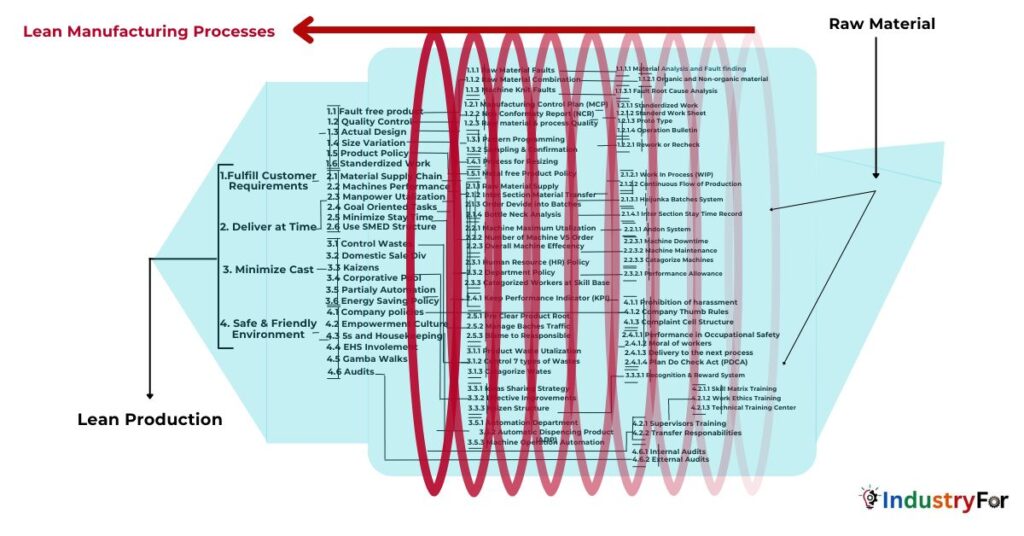
- Quality Production
- 1.1 Fulfill Customers Requirments
- 1.1.1 Faults Free and Quality Products
- 1.1.2 Raw Material Combination
- 1.1.3 Machine Knit Faults
- 1.1.3.1 Fault Root Cause Analysis
- 1.2 Quality Management System (QMS)
- 1.2.1 Product Quality Tools
- 1.2.1.1 Built-In Quality (BIQ)
- 1.2.1.2 Non-Conformity Report (NCR)
- 1.2.1.3 Work Order & Work Permit
- 1.2.1.4 Prototype
- 1.2.1.5 Operation Bullitin
- 1.2.2 Process Quality Tools
- 1.2.2.1 Manufacturing Control Plan (MCP)
- 1.2.2.2 Product and Tools Policies
- 1.2.2.3 Equipment Standardization
- 1.2.2.3.1 Machines Standardization
- 1.2.2.3.2 Tools Standardization
- 1.2.2.4 Standardized Work and Sheet
- 1.2.1 Product Quality Tools
- 1.3 Non-Conformity Reports (NCR)
- 1.4 Product Material Nature
- 1.1 Fulfill Customers Requirments
Deliver on Time
2. Deliver on Time
- 2.1 Material Supply Chain
- 2.1.1 Raw Material Supply
- 2.1.2 Inter-Section Material Transfer Advice (MTA)
- 2.1.3 Order Divided into Batches
- 2.1.3.1 Heijunka Batches System
- 2.1.4 Bottle Neck Analysis
- 2.1.4.1 Intersection Stay Time Record
- 2.2 Machine Performance
- 2.2.1 Machine Maximum Utilization
- 2.2.2 Number of Machines vs Order
- 2.2.3 Overall Machine Efficiency
- 2.2.3.1 Machine Downtime
- 2.2.3.2 Machine Maintenance
- 2.2.3.3 Categorize Machines
- 2.3 Manpower Utilization
- 2.3.1 Human Resource (HR) Policy
- 2.3.2 Department Policy
- 2.3.2.1 Performance Allowance
- 2.3.3 Categorize Workers at Skill Base
- 2.4 Goal-Oriented Tasks
- 2.4.1 Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
- 2.4.2 PDCA Fault Control Strategy
- 2.4.3 Department Target Tasking
- 2.5 Minimize Stay Time
- 2.5.1 Pre Clear Product Root
- 2.5.2 Manage Bachelorette Traffic
- 2.5.3 Blame the Responsible
- 2.6 Use SMED Structure
Minimize Cast
3. Industrial Cast Control System
- 3.1 Control of Waste
- 3.1.1 Product Waste Utilization
- 3.1.2 Control 7 types of Wastes
- 3.1.3 Categorize Wates
- 3.2 Recycle/Reuse Waste
- 3.3 Kaizen
- 3.3.1 Ideas Sharing Strategy
- 3.3.2 Effective Improvements
- 3.3.3 Kaizen Structure (PDCA)
- 3.4 Corporate Pool
- 3.5 Partially Automated
- 3.5.1 Automation Department
- 3.5.2 Automatic Dispensing Product (ADP)
- 3.5.3 Machine Operation Automation
- 3.6 Energy Saving Policy
Safe & Friendly Environment
4. Create a Safe & Friendly Environment for workers
- 4.1 Company policies
- 4.2 Empowerment Culture
- 4.2.1 Supervisors Training
- 4.2.1.1 Skill Matrix Training
- 4.2.1.2 Work Ethics Training
- 4.2.1.3 Technical Training Center
- 4.2.2 Transfer Responsibilities
- 4.2.1 Supervisors Training
- 4.3 5s (Five S)
- 4.4 EHS Rules
- 4.5 Gamba Walks
- 4.6 Audits
- 4.6.1 Internal Audits
- 4.6.2 External Audits
If you implement the above-given tools, techniques, roles, and regulations, you may achieve your Lean manufacturing and Lean production goals and grow your business to upscale in the market.
